Product description
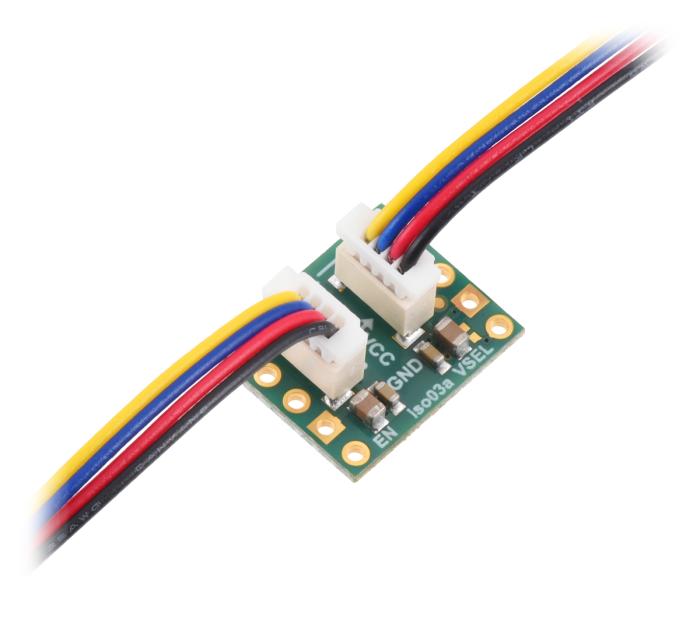
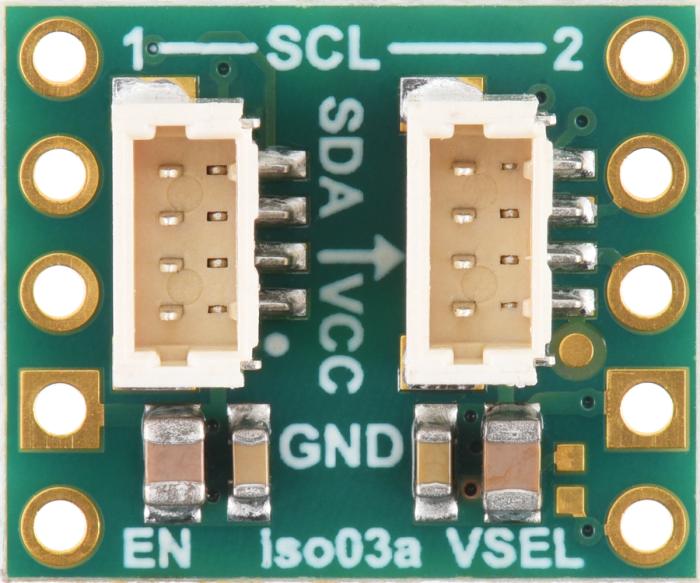
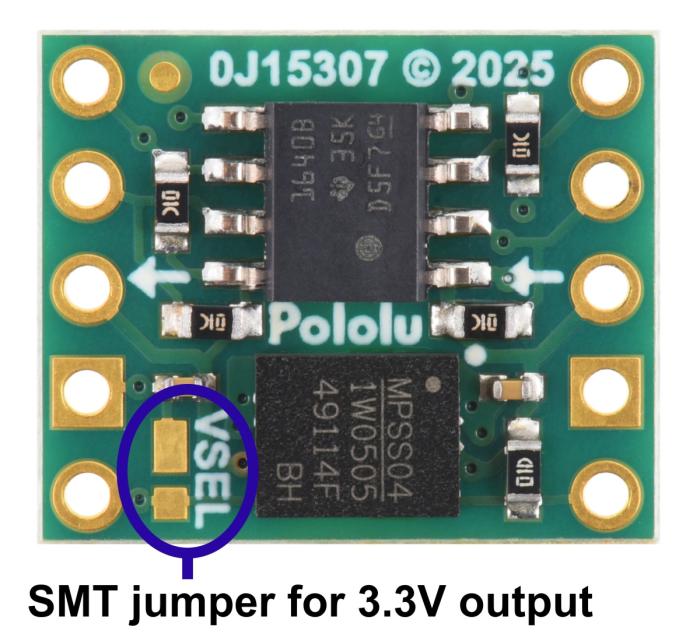
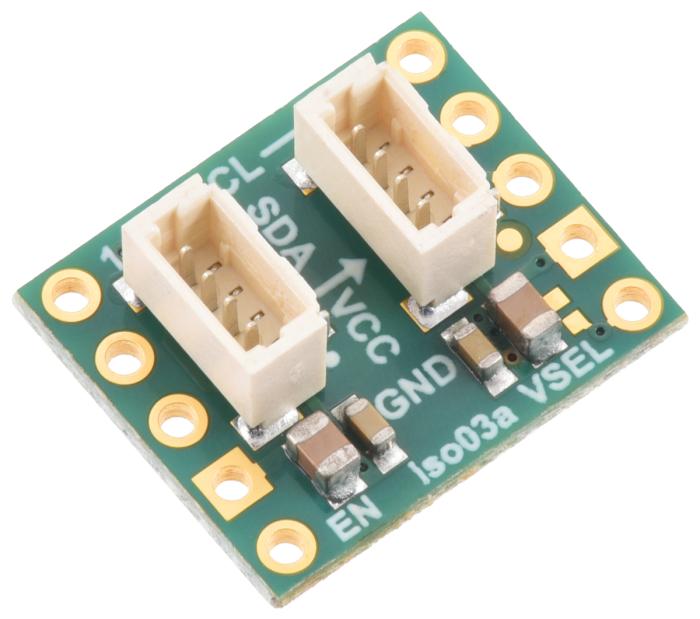
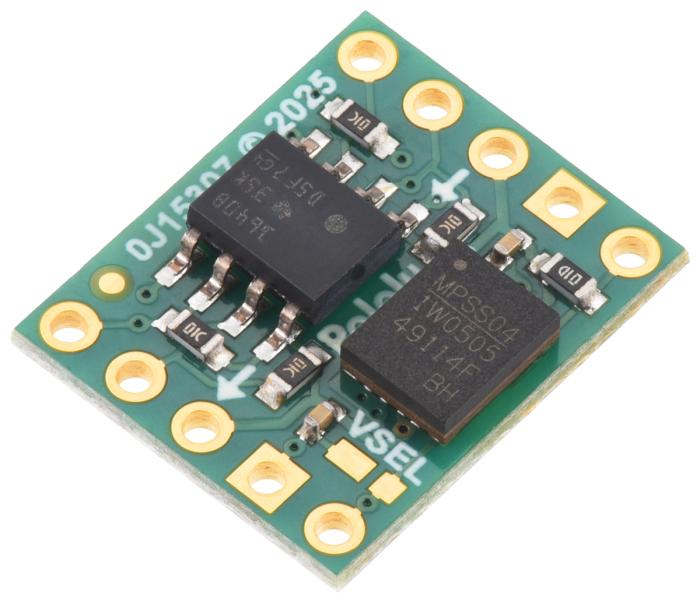
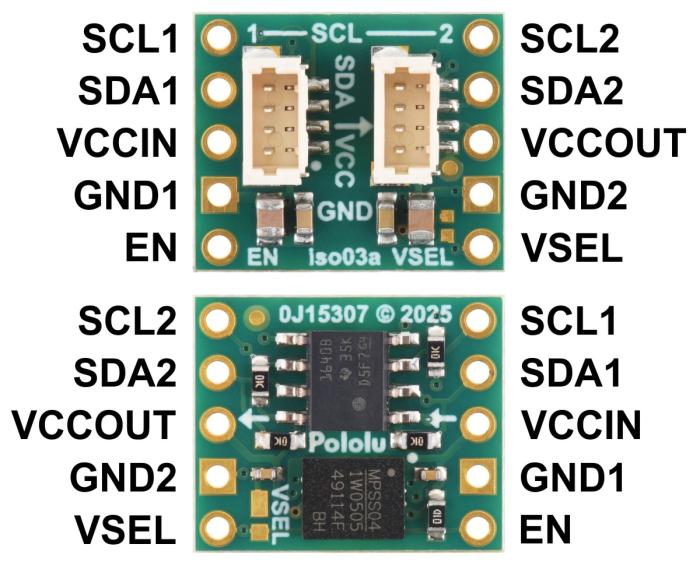
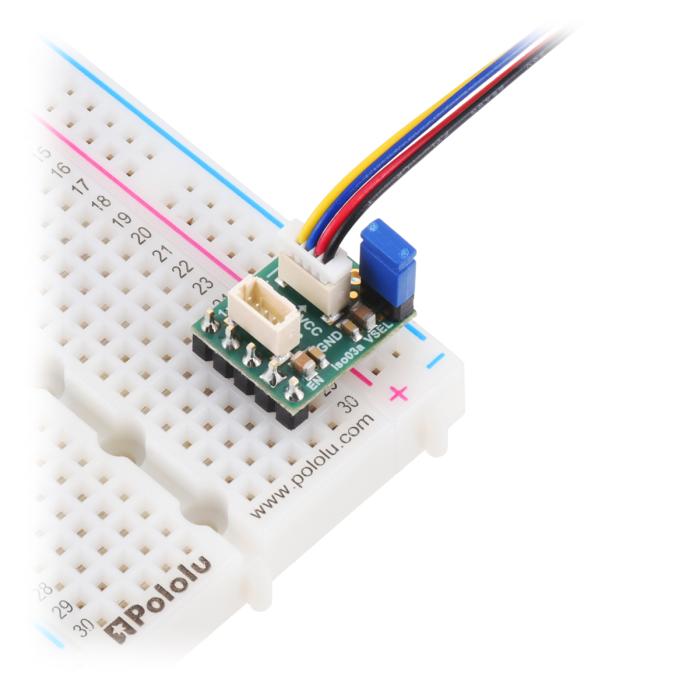
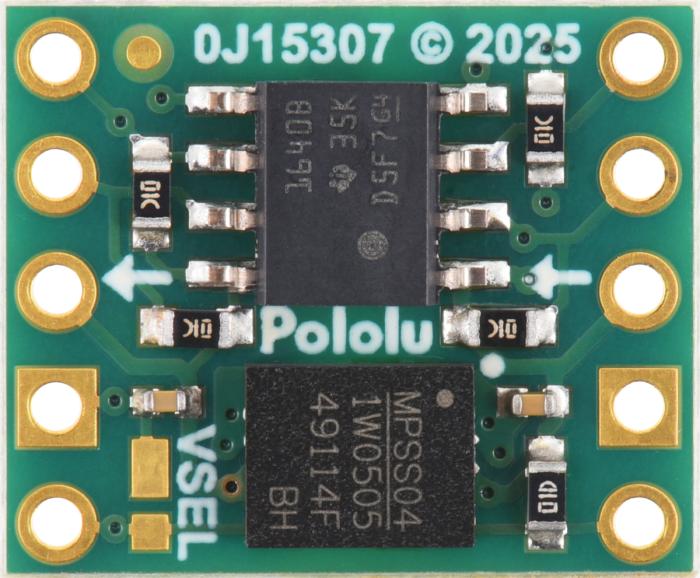
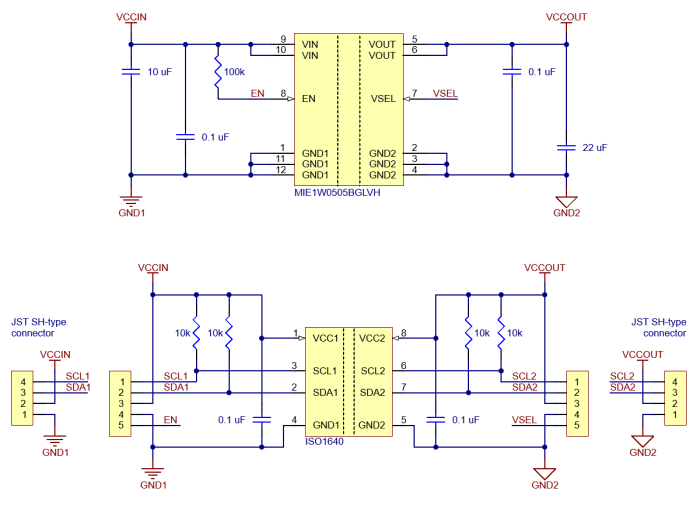
Pololu I2C Isolator with Isolated Power and Qwiic connectors - 3.3/5V 200mA. The purpose of this module is to provide galvanic isolation between two I2C domains while supplying the isolated side with a regulated voltage. The module allows full bidirectional I2C communication, including clock stretching. It uses Texas Instruments’ ISO1640B chip for signal isolation and an integrated DC-DC converter (MIE1W0505BGLVH) for power transfer. Everything is integrated on a compact PCB with Qwiic-compatible connectors.
Specifications:
- Input voltage (VCCIN): 3.0–5.5 V
- Output voltage (VCCOUT): 5 V by default, 3.3 V selectable via VSEL
- Maximum output current: approximately 180 mA continuous (200 mA peak) at 5 V input
- At 3 V input: 3.3 V output with approximately 75 mA continuous
- Data rate: up to 1.7 MHz
- Built-in pull-up resistors: 10 kohm on both sides
- Isolation (chip): up to 3 kV RMS (PCB clearance approximately 2 mm)
- Dimensions: approximately 12.7 x 15.2 mm
- Connectors: 2x JST SH 4-pin (Qwiic/STEMMA QT compatible)
- Protection: overtemperature and short-circuit protection for the DC-DC converter
Functional testing:
When tested with 5 V input and 5 V output, the module operated as specified. Two microcontroller systems could communicate over the I2C bus without interference or ground loop issues. Clock stretching worked as intended.
With a 150 mA load on the output, the voltage remained stable around 5 V. At 180–200 mA, heat generation increased, and efficiency decreased. With 3 V input and 3.3 V output, the maximum continuous load was around 70–75 mA before thermal protection activated.
When measuring I2C speed, communication was stable up to 1.5 MHz. At 1.7 MHz, the signals became slightly rounded, but communication remained functional. For higher speeds, external pull-up resistors were required to maintain sufficient signal strength.
The output on side 1 did not reach 0 V but stayed around 0.5–0.7 V at low level. The logic on that side must therefore tolerate this residual voltage.
Limitations:
- The PCB clearance limits the practical isolation distance to about 2 mm.
- The efficiency of the DC-DC converter is relatively low, resulting in some heat generation.
- Maximum load is limited to about 180 mA at 5 V, which is not sufficient for driving heavier loads.
- Continuous operation near maximum load requires ventilation or cooling.
Usability:
The module is easy to integrate thanks to its Qwiic connectors and compact form factor. It is useful in systems requiring isolation between microcontrollers and sensors or where ground potentials differ. The ability to select between 3.3 V and 5 V output makes it flexible for various logic levels.
Conclusion:
The Pololu ISO1640 with isolated power supply is a well-designed solution for galvanic isolation of I2C buses. It operates reliably within its specified limits, provides adequate isolation for most laboratory and embedded applications, and simplifies design by combining signal and power isolation.
It is especially suitable for systems with moderate current consumption on the isolated side where ground loops or interference need to be avoided. The main limitations are its modest output power and the need for heat management under higher loads.